制作 tensorflow 的数据集。
参考资料
北京大学人工智能实践:Tensorflow笔记
tensorflow TFRecords文件的生成和读取方法
tfrecords文件
tfrecords 是一种二进制文件,可以先将图片和标签制作成该格式的文件。使用 tfrecords 进行数据读取,会提高内存的利用率.
TFRecords是一种tensorflow的内定标准文件格式,其实质是二进制文件,遵循protocol buffer(PB)协议,其后缀一般为tfrecord。TFRecords文件方便复制和移动,能够很好的利用内存,无需单独标记文件,适用于大量数据的顺序读取,是tensorflow“从文件里读取数据”的一种官方推荐方法!
用 tf.train.Example 的协议存储训练数据。训练数据的特征用键值对的形式表示。
如:
'img_raw' : 值
'label' : 值 值是 Byteslist/FloatList/Int64List
用 SerializeToString() 把数据序列转化为字符串存储。
TFRecords文件的生成
其源代码主要位于文件tensorflow/python/lib/io/tf_record.py
官方例程tensorflow/examples/how_tos/reading_data/convert_to_records.py
第一步,生成TFRecord Writer
writer = tf.python_io.TFRecordWriter(path, options=None)
path:TFRecord文件的存放路径;
option:TFRecordOptions对象,定义TFRecord文件保存的压缩格式;
有三种文件压缩格式可选,分别为
TFRecordCompressionType.ZLIB
TFRecordCompressionType.GZIP
TFRecordCompressionType.NONE,默认为最后一种,即不做任何压缩,定义方法如下:
option = tf.python_io.TFRecordOptions(tf.python_io.TFRecordCompressionType.ZLIB)
第二步,tf.train.Feature生成协议信息
一个协议信息特征(这里翻译可能不准确)是将原始数据编码成特定的格式,一般是features中又包含feature,内层feature是一个字典值,它是将某个类型列表编码成特定的feature格式,而该字典键用于读取TFRecords文件时索引得到不同的数据,某个类型列表可能包含零个或多个值,列表类型一般有BytesList, FloatList, Int64List,通常用如下方法来生成某个列表类型再送给内层的tf.train.Feature编码:
tf.train.BytesList(value=[value]) # value转化为字符串(二进制)列表
tf.train.FloatList(value=[value]) # value转化为浮点型列表
tf.train.Int64List(value=[value]) # value转化为整型列表
其中,value是你要保存的数据。
内层feature编码方式:
feature_internal = {
"width":tf.train.Feature(int64_list=tf.train.Int64List(value=[width])),
"weights":tf.train.Feature(float_list=tf.train.FloatList(value=[weights])),
"image_raw":tf.train.Feature(bytes_list=tf.train.BytesList(value=[image_raw]))
}
外层features再将内层字典编码:
features_extern = tf.train.Features(feature_internal)
看起来,tf.train.Feature这个接口可以编码封装列表类型和字典类型,但注意用的接口是不一样的,内层用的是tf.train.Feature而外层用的是tf.train.Features,一个是对单一数据编码成单元feature,而另一个是将包含多个单元feature的字典数据再编码为集成的features。
第三步,使用tf.train.Example将features编码数据封装成特定的PB协议格式
example = tf.train.Example(features_extern)
第四步,将example数据系列化为字符串
example_str = example.SerializeToString()
第五步,将系列化为字符串的example数据写入协议缓冲区
writer.write(example_str)
TFRecordWriter拥有类似python文件操作的接口,如writer.flush()立即将内存数据刷新到磁盘文件里,writer.close()关闭TFRecordWriter,在写完数据到协议缓冲区后通常需要调用writer.close()主动关闭TFRecords文件操作接口。
举例说明TFRecords文件的生成
下面的例子可以将如下图片生成TFRecords文件,我们将保存该图片的宽高以及其内容,并保存浮点型数据9.99、8.88、6.66到不同的压缩tfrecord文件里,该图片的原始大小是1.2Mb,等下我们看一下不同TFRecords文件压缩方式生成文件的大小。

代码及其注释如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
| import tensorflow as tf
filename = "/home/xsr-ai/study/tfrecord/beautiful_view.jpg"
image = tf.read_file(filename)
image_jpeg = tf.image.decode_jpeg(image, channels=3, name="decode_jpeg_picture")
image_jpeg = tf.reshape(image_jpeg, shape=(2500,2000,3))
img_shape = image_jpeg.shape
width = img_shape[0]
height = img_shape[1]
sess = tf.Session()
image = sess.run(image)
sess.close()
path_none = "/home/xsr-ai/study/tfrecord/img_compress_none.tfrecord"
path_zlib = "/home/xsr-ai/study/tfrecord/img_compress_zlib.tfrecord"
path_gzip = "/home/xsr-ai/study/tfrecord/img_compress_gzip.tfrecord"
options_zlib = tf.python_io.TFRecordOptions(tf.python_io.TFRecordCompressionType.ZLIB)
options_gzip = tf.python_io.TFRecordOptions(tf.python_io.TFRecordCompressionType.GZIP)
writer_none = tf.python_io.TFRecordWriter(path_none, options=None)
writer_zlib = tf.python_io.TFRecordWriter(path_zlib, options=options_zlib)
writer_gzip = tf.python_io.TFRecordWriter(path_gzip, options=options_gzip)
feature_internal_none = {
"float_val":tf.train.Feature(float_list=tf.train.FloatList(value=[9.99])),
"width":tf.train.Feature(int64_list=tf.train.Int64List(value=[width])),
"height":tf.train.Feature(int64_list=tf.train.Int64List(value=[height])),
"image_raw":tf.train.Feature(bytes_list=tf.train.BytesList(value=[image]))
}
feature_internal_zlib = {
"float_val":tf.train.Feature(float_list=tf.train.FloatList(value=[8.88])),
"width":tf.train.Feature(int64_list=tf.train.Int64List(value=[width])),
"height":tf.train.Feature(int64_list=tf.train.Int64List(value=[height])),
"image_raw":tf.train.Feature(bytes_list=tf.train.BytesList(value=[image]))
}
feature_internal_gzip = {
"float_val":tf.train.Feature(float_list=tf.train.FloatList(value=[6.66])),
"width":tf.train.Feature(int64_list=tf.train.Int64List(value=[width])),
"height":tf.train.Feature(int64_list=tf.train.Int64List(value=[height])),
"image_raw":tf.train.Feature(bytes_list=tf.train.BytesList(value=[image]))
}
features_extern_none = tf.train.Features(feature=feature_internal_none)
features_extern_zlib = tf.train.Features(feature=feature_internal_zlib)
features_extern_gzip = tf.train.Features(feature=feature_internal_gzip)
example_none = tf.train.Example(features=features_extern_none)
example_zlib = tf.train.Example(features=features_extern_zlib)
example_gzip = tf.train.Example(features=features_extern_gzip)
example_str_none = example_none.SerializeToString()
example_str_zlib = example_zlib.SerializeToString()
example_str_gzip = example_gzip.SerializeToString()
writer_none.write(example_str_none)
writer_zlib.write(example_str_zlib)
writer_gzip.write(example_str_gzip)
writer_none.close()
writer_zlib.close()
writer_gzip.close()
print("finish to write data to tfrecord file!")
|
运行代码后,生成的数据如下:
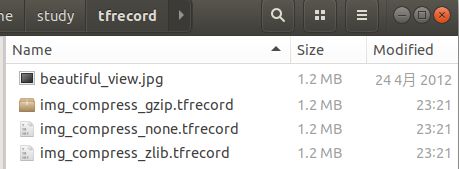
我们看到,用不同方式压缩保存的tfrecord文件大小并无异,这可能是数据量不够多的缘故。
ps:我运行的时候,有报错,但是不影响使用,还是生成了三个文件。
TFRecords文件的读取
TFRecords文件的读取主要是使用tf.TFRecordReader和tf.python_io.tf_record_iterator
其源代码位于tensorflow/python/ops/io_ops.py和tensorflow/python/lib/io/tf_record.py
第一步,使用tf.train.string_input_producer生成文件队列
filename_queues = tf.train.string_input_producer([tfrecord_path_none,tfrecord_path_zlib,tfrecord_path_gzip])
第二步,生成TFRecord Reader
reader = tf.TFRecordReader(name=None, options=None)
options是tfrecord文件存储时的压缩方式,与tf.python_io.TFRecordWriter保存时一致,是一个TFRecordOptions对象。
第三步,读取tfrecord文件
serialized_example = reader.read(filename)
filename是tf.train.string_input_producer得到的文件队列名,读取得到的是一个系列化的example。
第四步,使用tf.parse_single_example解析得到的系列化example
features = tf.parse_single_example(
serialized_example,
features={
"float_val":tf.FixedLenFeature([], tf.float),
"width":tf.FixedLenFeature([], tf.int64),
"height":tf.FixedLenFeature([], tf.int64),
"image_raw":tf.FixedLenFeature([], tf.string)
}
)
需要按照存储时的格式还原features,必须写明features内的字典的键索引得到特定的数据!
第五步,处理得到的数据
features是一个字典,要使用特定数据,需要用字典的key来索引得到相应的数据,如要得到的width的值,则可以以features[‘width’]得到,对于得到的数据还需要做一些处理的,比如features[‘image_raw’]需要decode才能显示整个图片。
举例说明TFRecords文件的读取
我们根据生成的tfrecord文件来读取其中的float_val的值,并显示image_raw的图片内容。
代码及其注释如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
| import tensorflow as tf
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
tfrecord_path_none = "/home/xsr-ai/study/tfrecord/img_compress_none.tfrecord"
tfrecord_path_zlib = "/home/xsr-ai/study/tfrecord/img_compress_zlib.tfrecord"
tfrecord_path_gzip = "/home/xsr-ai/study/tfrecord/img_compress_gzip.tfrecord"
filename_queues = tf.train.string_input_producer([tfrecord_path_none,tfrecord_path_zlib,tfrecord_path_gzip])
options_zlib = tf.python_io.TFRecordOptions(tf.python_io.TFRecordCompressionType.ZLIB)
options_gzip = tf.python_io.TFRecordOptions(tf.python_io.TFRecordCompressionType.GZIP)
reader_none = tf.TFRecordReader(options=None)
reader_zlib = tf.TFRecordReader(options=options_zlib)
reader_gzip = tf.TFRecordReader(options=options_gzip)
_,serialized_example_none = reader_none.read(filename_queues)
_,serialized_example_zlib = reader_zlib.read(filename_queues)
_,serialized_example_gzip = reader_gzip.read(filename_queues)
features_none = tf.parse_single_example(serialized_example_none,
features={
"float_val":tf.FixedLenFeature([], tf.float32),
"width":tf.FixedLenFeature([], tf.int64),
"height":tf.FixedLenFeature([], tf.int64),
"image_raw":tf.FixedLenFeature([], tf.string)
})
features_zlib = tf.parse_single_example(serialized_example_zlib,
features={
"float_val":tf.FixedLenFeature([], tf.float32),
"width":tf.FixedLenFeature([], tf.int64),
"height":tf.FixedLenFeature([], tf.int64),
"image_raw":tf.FixedLenFeature([], tf.string)
})
features_gzip = tf.parse_single_example(serialized_example_gzip,
features={
"float_val":tf.FixedLenFeature([], tf.float32),
"width":tf.FixedLenFeature([], tf.int64),
"height":tf.FixedLenFeature([], tf.int64),
"image_raw":tf.FixedLenFeature([], tf.string)
})
image = tf.image.decode_jpeg(features_gzip['image_raw'], channels=3)
coord = tf.train.Coordinator()
threads = tf.train.start_queue_runners(sess=sess, coord=coord)
sess = tf.Session()
image,float_val_none,float_val_zlib,float_val_gzip = sess.run([image, features_none['float_val'], features_zlib['float_val'], features_gzip['float_val']])
coord.request_stop()
coord.join(threads)
sess.close()
print(float_val_none)
print(float_val_zlib)
print(float_val_gzip)
plt.imshow(image)
plt.title("beautiful view")
plt.show()
print("finish to read data from tfrecord file!")
|

